Medical images are often affected by noise or artifacts. A MOX research topic concerns the reduction of metal artifacts (MAR) in X-ray computerized tomography (CT), and the development of techniques and procedures for the pre-processing of medical images. A second focus is the generation of automatic methods for the segmentation of different vessel district […]
Monthly Archives: January 2022
The cardiac insufficiency (CI) represents the main cause of hospitalization after the age of 65 years, and the related mortality is very high. There is nowadays a big interest in this pathology in order to find efficient therapies. In particular, a great attention has been done to the ventricular dissincrony (VD) […]
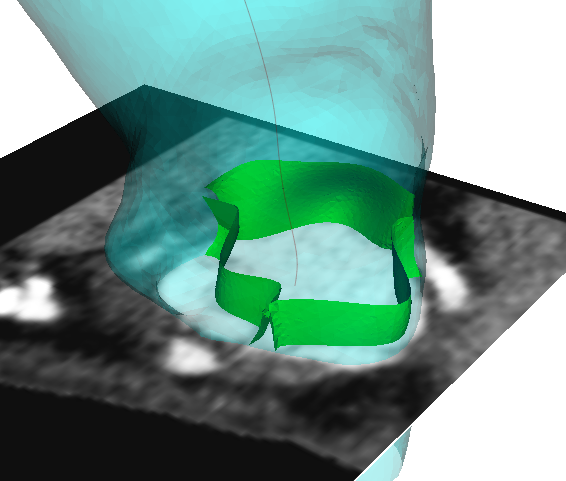
Nowadays ventricular assist devices (VAD) play an important role in the treatment of terminal heart failure. While the devices themselves have been widely studied there are no studies of patient-specific numerical simulation in this context. This could be explained by the fact that the presence of the device induces metallic artifacts and […]
The presence of stent in aortic bioprostesis have been shown to increase stresses on the valve leaflets and to reduce dynamic root motion during the cardiac cycle. The research focused on the comparison of the forces developed in the aortic root after aortic valve replacement with stented or stentless bioprosthesis. To this aim fluid-structure […]
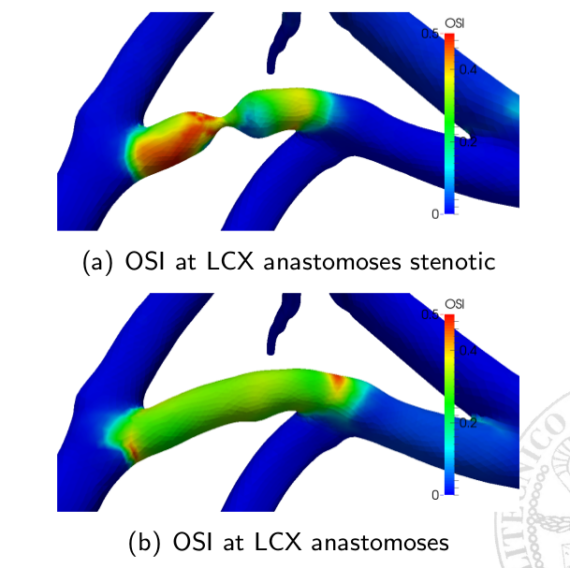
It is well known that Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) failure in the long term is mainly due to restenosis, which can be related to sub-optimal haemodynamical conditions near the grafts. Under this assumption, the research at MOX aims to a better understanding of CABG effects on coronary circulation and possibly to […]
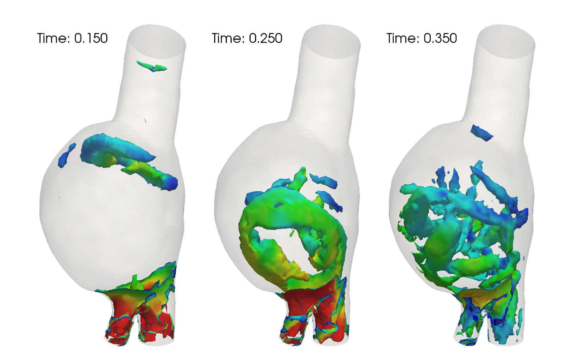
Bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) is the most common congenital heart disease. Itis related to an increased prevalence of ascending aortic dilatation and aneurysm in normally functioning valvular regime when compared to tricuspid aortic valve (TAV). The pathogenesis of aortic dilatation in patients with BAV is nowadays uncertain. A first hypothesis postulates a genetic origin for these […]
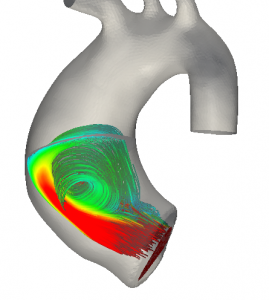
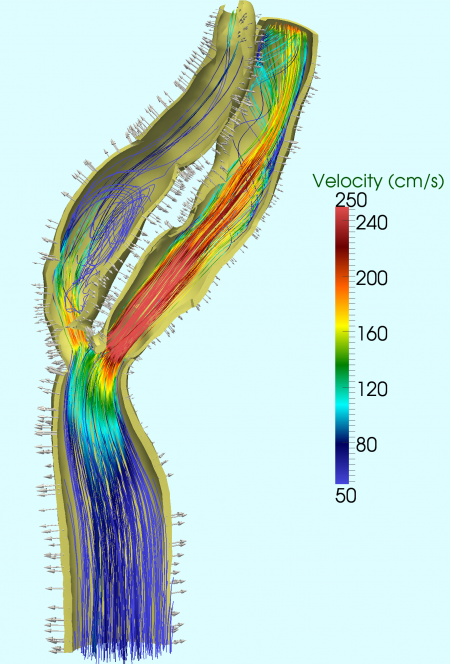
The carotid bifurcation is one of the preferential site of plaque formation, leading to vessel stenosis, and, possibly, to a complete obstruction of the vessel, formation of blood clots and breakage with embolization of fragments into the brain tissue. For these reasons, carotid endarterectomy (CEA), consisting in the surgical removal of the plaque, is intensively used in the clinical practice. The research […]
The abdominal aorta is one of the preferential site of aneurysm formation. Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) represent 83 % of all non-cerebral aneurysms diagnosed in the United States. Untreated AAAs may rupture a severe clinical event associated with high rate of mortality and morbidity. The research at MOX focused on the fluid-dynamics in AAA. In […]
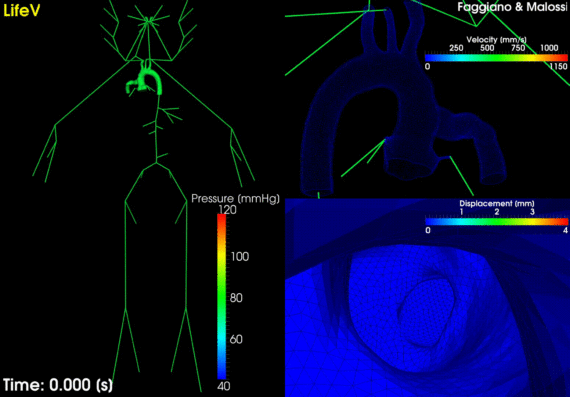
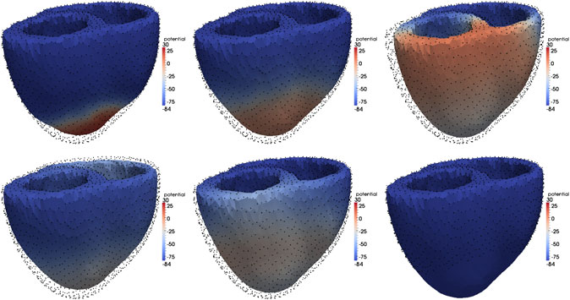
Electromechanical coupling Modeling the heart contraction leads to the solution of a coupled problem between the electrical model, which describes the propagation of the electrical signal that triggers the heart contraction, and the mechanical model, that describes the cardiac deformations. Beside the direct effect of the electrical activity in the mechanics, it is relevant to model also the feedback of the mechanics in the […]
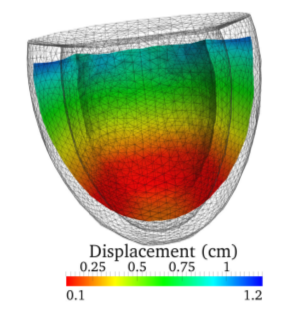
Cardiac deformations are described by the equations of continuum mechanics, where the myocardium is considered as orthotropic, hyperelastic, and incompressible with passive properties defined by an exponential strain energy function. Several studies have underlined the mechanical importance of the alignment of cardiac cells and of the structure of collagen sheets. This is […]